Injecting testosterone is a critical aspect of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), and it is essential to do it safely and effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will provide a step-by-step tutorial on how and where to inject testosterone. Additionally, we will explore common side effects and how to manage them, ensuring a smooth and successful TRT experience.
Importance of Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Before we dive into the specifics of administering testosterone injections, let’s briefly touch upon why TRT is crucial for many individuals. Testosterone is a vital hormone responsible for various functions in the body, including muscle development, bone density, mood regulation, and sexual health. When testosterone levels drop below the normal range, individuals may experience fatigue, depression, loss of muscle mass, and decreased libido. TRT can help restore these levels, improving overall well-being.
Types of Testosterone Injections
Before you can administer a testosterone injection, it’s essential to understand the different types available. Testosterone injections typically come in two forms: intramuscular (IM) and subcutaneous (SC).
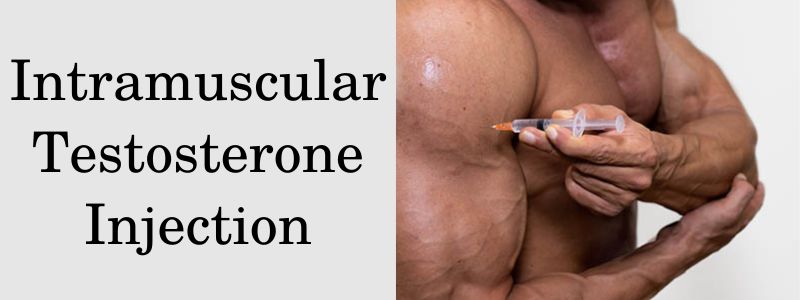
Intramuscular Injections (IM)
Intramuscular injections involve injecting testosterone directly into a muscle, typically the gluteus maximus (buttocks) or the deltoid muscle (upper arm). This method allows for slow and sustained release of testosterone into the bloodstream. Many patients prefer IM injections due to their infrequent dosing schedule.
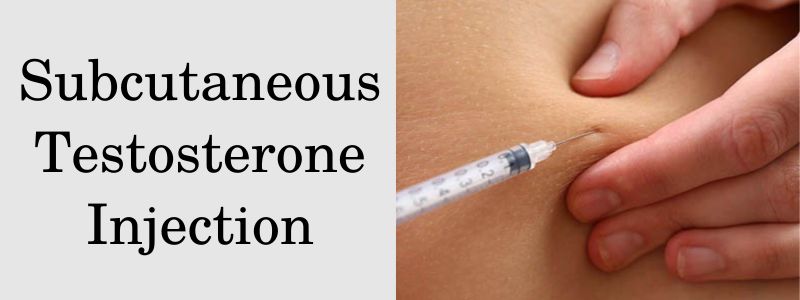
Subcutaneous Injections (SC)
Subcutaneous injections, on the other hand, deliver testosterone just beneath the skin into the fatty tissue. The most common injection site for SC injections is the abdominal area, specifically around the navel. SC injections are less painful than IM injections and may be preferred by some individuals.
Preparing for the Injection
Before you begin the injection process, it’s crucial to gather all the necessary supplies and create a clean and sterile environment. Here’s what you’ll need:
Supplies:
- Testosterone vial: Ensure it is the correct type and dosage prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Needle and syringe: Choose the appropriate gauge and length of the needle based on your injection method.
- Alcohol pads: Used for cleaning the injection site and vial stopper.
- Cotton balls or gauze: For applying pressure after the injection.
- Sharps container: A secure disposal container for used needles and syringes.
Steps to Prepare:
- Wash your hands: Start by thoroughly washing your hands with soap and water to reduce the risk of infection.
- Clean your workspace: Ensure your workspace is clean and well-lit. Lay out all your supplies within reach.
- Check the expiration date: Examine the testosterone vial to confirm that it has not expired. Do not use an expired vial.
- Draw up the correct dosage: Use the syringe to draw up the prescribed dosage of testosterone from the vial.
- Remove air bubbles: Gently tap the syringe to remove any air bubbles, and then push the plunger slightly to release them.
Where to Inject Testosterone
The choice of injection site depends on whether you are administering an intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.
Intramuscular Injection Sites
Gluteus Maximus (Buttocks). This is one of the most common sites for IM injections. To locate the injection site, divide the buttock into four quadrants and choose the upper, outer quadrant. Clean the area with an alcohol pad and inject at a 90-degree angle.
Deltoid Muscle (Upper Arm). For those comfortable with this site, it is an option for IM injections. Locate the midpoint of the upper arm between the shoulder and elbow, clean the area, and inject at a 90-degree angle.
Subcutaneous Injection Site
Abdomen. The abdomen is the primary site for subcutaneous injections. Start by identifying an area about two inches away from your navel and clean it with an alcohol pad. Inject at a 45-degree angle.
Administering the Injection
Now that you have prepared your supplies and chosen your injection site, it’s time to administer the testosterone injection.
Intramuscular Injection (IM)
- Position yourself: If you are injecting into the gluteus maximus, lie on your side with the upper buttock exposed. If injecting into the deltoid muscle, stand or sit comfortably.
- Insert the needle: Hold the syringe like a dart, and insert the needle quickly and firmly at the chosen site at a 90-degree angle.
- Aspirate (optional): Pull back slightly on the plunger to check for blood. If you see blood in the syringe, you have hit a blood vessel. Withdraw the needle and choose a different location.
- Inject the testosterone: If there’s no blood, slowly push the plunger to administer the testosterone.
- Remove the needle: Withdraw the needle at the same angle it was inserted.
- Apply pressure: Use a cotton ball or gauze to apply gentle pressure to the injection site to minimize bleeding.
Subcutaneous Injection (SC)
- Pinch the skin: Using your non-dominant hand, pinch a fold of skin around the cleaned injection site to create a small mound.
- Insert the needle: Hold the syringe at a 45-degree angle and insert the needle into the raised skin fold.
- Inject the testosterone: Slowly push the plunger to administer the testosterone.
- Remove the needle: Withdraw the needle at the same angle it was inserted.
- Release the skin: Let go of the pinched skin fold.
- Apply pressure: Use a cotton ball or gauze to apply gentle pressure to the injection site.
How to Manage Common Side Effects
While testosterone injections can be highly effective, they may also lead to some side effects. It’s essential to be aware of these potential issues and know how to manage them.
Pain and Discomfort at the Injection Site
It’s common to experience mild pain or discomfort after an injection. To alleviate this:
- Apply a cold pack to the injection site for a few minutes.
- Gentle massage of the area may help.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can be taken if recommended by your healthcare provider.
Injection Site Reactions
Some individuals may experience redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site. To address these reactions:
- Use an over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream as directed.
- If symptoms persist or worsen, contact your healthcare provider.
Mood Swings
Testosterone levels can fluctuate after an injection, leading to mood swings. To manage this:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Consider counseling or therapy if mood swings persist or affect your quality of life.
Acne and Oily Skin
Increased testosterone levels can lead to skin changes. To minimize acne and oily skin:
- Follow a consistent skincare routine.
- Use non-comedogenic products.
- Consult a dermatologist